Mobile Virtual Network Enablers: Winning in an increasingly crowded market
The MVNE Market Is Crowded
Today, MVNOs and MNOs are being served by a fragmented market of Mobile Virtual Network Enablers (MVNEs) ranging from large scale Global Vendors, System Integrators, and a large number of small specialist providers and niche players.
Figure 1 provides an overview of MVNE segments and select players in the market.
Source: Cartesian
MVNEs provide services to both MVNOs and MNOs through a number of common engagement models including:
- Providing MNOs with a standalone or integrated network / OSS / BSS stack to host sub-brands and MVNOs;
- Providing MNOs with a robust platform to host a growing portfolio of MVNOs – this may include migrating all or part of the existing MVNO subscriber base to a standalone platform;
- Enabling MVNOs seeking fast market entry through cloud-based delivery models; and
- Providing MVNOs with a combination of network, OSS, and BSS solution components, and value-added services to augment their propositions.
Trends in the MVNO Space Affecting the MVNE Market
The evolving needs of MVNOs present a wide range of opportunities for MVNEs, with MVNOs increasingly seeking a number of requirements:
- Full control and flexibility in order to operate autonomously from the host MNO;
- Richer experiences and value-added services for more meaningful market differentiation;
- Capability to support bespoke customer acquisition and retention strategies; and
- Flexible commercial models dependent on preference for OPEX vs. CAPEX
In response, MVNEs are extending their services beyond traditional OSS/BSS platform solutions such as the core OCS (Online Charging System), service fulfillment, network inventory management, service assurance, subscriber management, and channel management to serve these needs.
Full Control and Flexibility in Order to Operate Autonomously from the MNO
As MVNOs seek full control and flexibility, we are seeing a number of platform-related trends and developments in the market. The most prominent are outlined below.
- The Full MVNO model helps ensure flexibility and autonomy from the host MNO. Most MVNEs are now providing Core Network components to augment their OSS/BSS platform: services such as HLR/HSS, SMSC, GMSC, MME, IVR, GGSN, and PCRF solutions. This autonomy also delivers additional negotiation power with respect to renewing commercial terms with MNOs.
- The deployment of 4G services by MVNOs is accelerating. Large increases in bandwidth and data traffic are trends that are likely to continue and will impact the services provided by MVNEs.
- Policy management is increasingly important as MVNOs look to differentiate their service for specific niches through the use of differentiated tariffing and zero-rating for certain sites such as Facebook.
- MVNE services on cloud-based platforms are almost universally expected. Cloud-based platforms are reducing the time to market, increasing business flexibility, and enabling opex based utility charging.
- M2M/IoT markets continue to grow and M2M-focused MVNOs are looking to capitalize on this opportunity. Whilst this market still remains in its infancy, MVNEs are increasingly enhancing their platforms to serve the M2M/IoT markets.
- Seamless roaming and competitive rates across multiple geographies enabling MVNOs to effectively serve the IoT market and outbound roaming market for business and consumer travelers.
Richer Experiences and Value Added Services for More Meaningful Market Differentiation
MVNEs are bringing value-added services and applications to market to support their MNO and MVNO customers to differentiate in their respective markets. Value-added services in an MVNE portfolio will help differentiation and avoid MVNE services becoming commoditized.
- Data analytics capabilities are expanding in their sophistication and application. As more MVNOs move from basic reporting to business intelligence and predictive analytics, there is an opportunity for MVNEs to provide these services to support MVNOs across the customer lifecycle from acquisition to retention.
- 4G speeds are enabling OTT Mobile VOIP and WebRTC services such as real-time Voice, Video, Messaging into VoIP, Web & Mobile Apps. There is an increasing need for MVNEs to provide integration of these services with their platforms.
- Fraud and Revenue assurance is a capability that MVNEs may offer to MVNOs who are not looking to leverage specialized solutions or build as an in-house capability.
- Mobile Money, Mobile wallets, and payments are set to grow significantly together with remittances in emerging markets. Some players are already launching their own mobile wallet and payment solutions. For MVNEs this offers a potential opportunity to differentiate or target MVNOs with aspirations in financial services or emerging markets.
Capability to Support Bespoke Customer Acquisition and Retention Strategies
In order to seek gains in market share, MNOs and MVNOs are deploying customer acquisition strategies that target specific segments as well as strategies to retain customers by increasing customer stickiness via loyalty plays. Three key trends are discussed below.
- An increasing number of MNOs are launching one or more sub-brands. A sub-brand enables an MNO to target a niche customer segment separate from their main brand to test new market propositions, whilst preserving their primary brand value. MVNEs can potentially support MNOs with the launch and ongoing management of these sub-brands.
- To combat tightening margins, differentiate services, and create customer stickiness, some MVNOs are looking to non-telco revenue streams such as video on demand and content services to monetize their customer base. These opportunities require MVNEs to extend provisioning, billing, and care capabilities to new services as well as potentially offering white label VAS as part of the portfolio.
- There is a broad range of MVNOs targeting BYOD and enterprise. MVNEs supporting this trend will need to augment their service to allow for features such as fleet data sharing, application deployment and device management.
Winning in the MVNE Market
MVNE Proposition Elements
An MVNE’s proposition should enable an MNO or MVNO to address complexity and time of deployment, position itself to compete in the market, and improve its commercial outcomes. To deliver these benefits, there are ten key elements of an MVNE proposition ranging from consulting and project management at the start of an engagement, to core platform services, value-added services, and service wrap.
The ten proposition elements are shown in figure 2.

The proposition elements represent levers in which an MVNE can meet the evolving needs of MVNOs and MNOs.
- Platform elements of a proposition deliver MVNOs more control, flexibility, and autonomy from the MNO, as well capabilities to support acquisition and retention strategies via the launch of sub-brands and non-telco revenue streams.
- Value-added services offer benefits on two dimensions. Services such as WebRTC provide MVNOs an opportunity to deliver richer experiences to their customer base, while data analytics provide a platform for MVNEs to differentiate their services with actionable insights for MVNOs to optimize customer lifecycle management.
- A compelling service wrap provides an opportunity for an MVNE to differentiate its proposition by providing services to an MVNO and MNO with superior SLAs and KPIs, assurance that deployment will be managed effectively with launch timeframes that are significantly compressed.
Proposition Weaknesses Observed in Market
There are a number of common weaknesses in MVNEs propositions that need to be overcome. These weaknesses range from missing hygiene factors to inadequate levels of integration support, poor implementation planning, and inadequate service wrap (KPIs / SLAs).
Figure 3 highlights key areas of weaknesses observed in the market.

Source: Cartesian
Differentiating in Market Goes beyond Core Network
In order to compete in the market, MVNEs are differentiating beyond the core network, OSS, and BSS components. MVNEs are differentiating on service wrap with superior SLAs to deliver greater speed to market, scalability, and the ability to quickly turn on quickly new services. Several MVNEs are offering strategic pricing to address emerging market ARPUs, whilst others are starting to offer alternative commercial models such as taking ownership interest in MVNO customers.
As an example, high levels of virtualization, pre-integration of solutions, and robust planning and deployment frameworks enable MVNOs to reduce the time-to-market to several months from the point of contract sign-off. Removing the need to partition an existing MNO’s platform with an “off the shelf” product removes the need for complex integration and migration of customers.
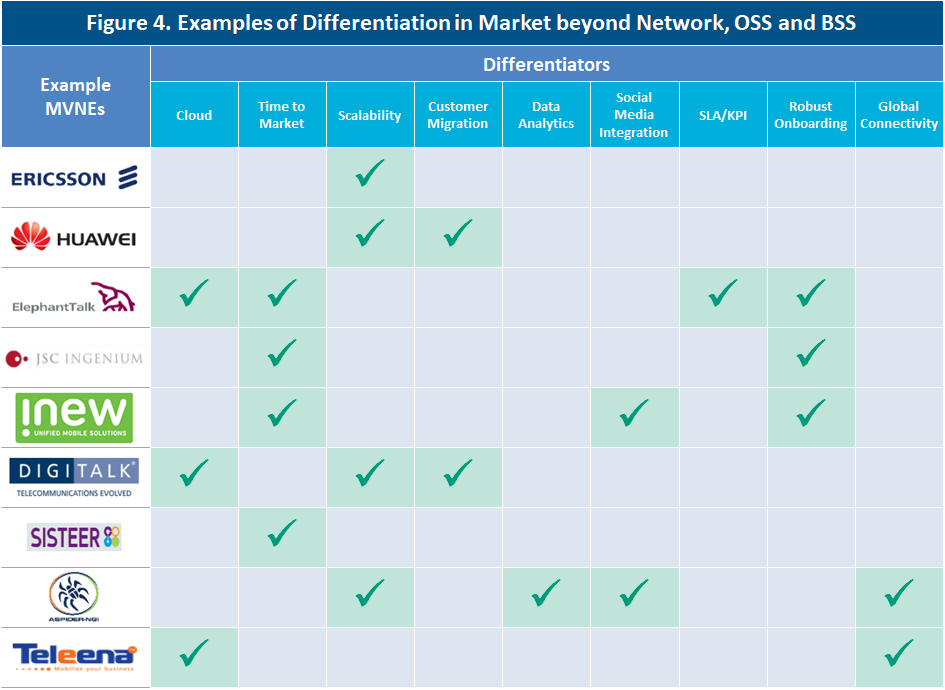
MVNEs can also deploy differentiation strategies aimed at delivering value-added services which enable enhanced experience for the MNO/MVNO and subsequently their customers. Some areas of differentiation may include data analytics modules, integration with social media, simplified/augmented platforms for emerging markets and global connectivity. What is clear is that there is no universal approach in the market, with MVNEs pursuing a range of strategies for differentiation.
Figure 4 illustrates how the approach to differentiation varies by MVNE.
Conclusion
The MVNE market is crowded and competition is intense in an industry where margins and value are already under immense pressure.
In order to differentiate, MVNEs should align portfolios and development roadmaps to respond to the changing needs of MNOs and MVNOs. Key areas of opportunity include reducing the time to market, increasing value-added services, and more generally allowing business to be conducted simply, efficiently, and more cost-effectively. Additionally, we will see MVNEs continue to expand internationally as they seek to capture new MVNO opportunities in LATAM, Africa, Asia and the Middle East.<>




